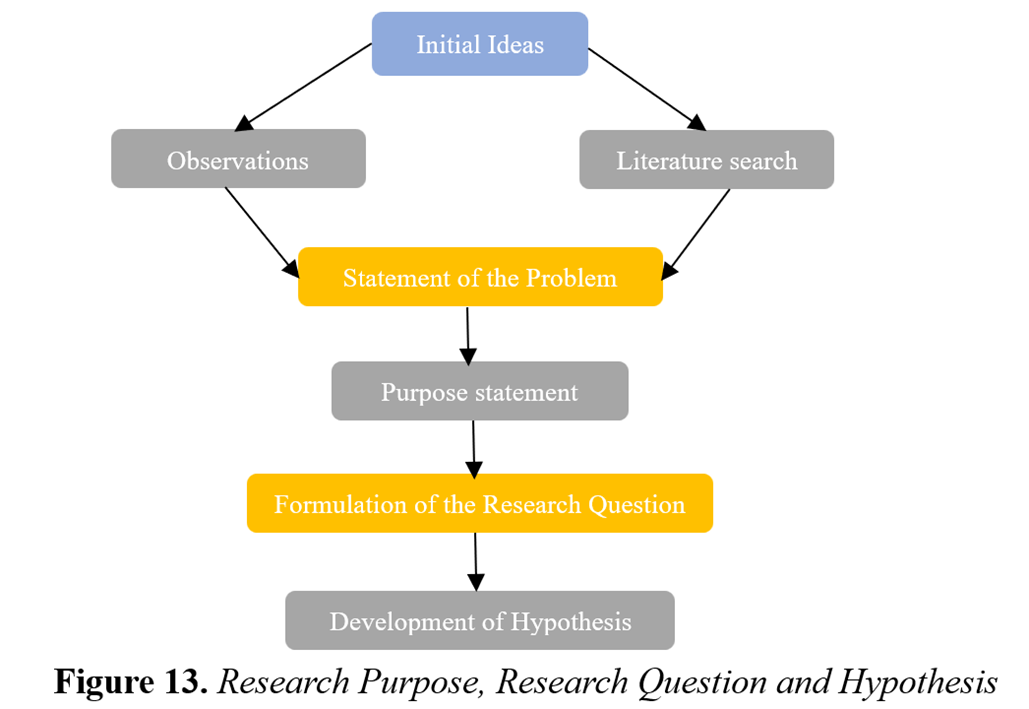
A research design is a foundation for data collection and analysis in a study. It outlines the methods and procedures, serving as a blueprint for measuring and analysing data. This strategy enables investigators to investigate research questions and arrange the conditions for data collection and analysis in a manner that permits the findings of a sample to be generalised to the larger population (Pandey & Pandey, 2015).
Choosing the appropriate research design is crucial while conducting research. It involves considering various factors, from broader assumptions to specific data collection and analysis techniques. It is essential to note that there is no fixed order for making these decisions, and they should depend on what is most relevant to your research objectives.
Research approaches consist of many plans and procedures that guide the steps from broader assumptions to detailed data collection, analysis, and interpretation methods. When selecting an approach to study a topic, you need to consider the philosophical assumptions, procedures of inquiry (research designs), and specific research methods of data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Your choice of a research approach should be informed by the nature of the research problem or issue, your personal experiences, and the intended audience. These three elements - research approaches, research designs, and research methods - provide a framework for understanding the perspective of research.
Ultimately, your research design will depend on various factors, such as the problem or issue you are investigating, your personal experiences, and the audience you intend to reach. For instance, quantitative research may be the most suitable approach if you aim to test objective theories by examining the relationship between variables. This method involves measuring variables using instruments, which generates numerical data that can be analysed using statistical methods (Creswell, 2014).
A design or structure must be established to begin data collection or analysis in social research. However, a research design is more than just a work plan. While a work plan outlines the steps necessary to complete a project, it is based on the research design. Essentially, the function of a research design is to ensure that the evidence collected allows us to answer the initial question clearly.
It is important to note that research design is a logical problem rather than a logistical one. In social research, factors such as sampling, data collection method, and question design are all subsidiary to the question of what evidence needs to be collected. Unfortunately, many researchers jump into designing questionnaires or conducting interviews before considering what information they need to answer their research questions.
It is also essential to distinguish between the research design and the data collection method. The data collection method has no bearing on the logic of the design. Explanatory research seeks to develop and evaluate causal theories, but in social sciences, causation is probabilistic rather than deterministic. This is why the role of research design is so crucial - it minimises the likelihood of drawing incorrect causal inferences from data. When designing research, the type of evidence needed to answer the research question convincingly must be identified.