Summary: Focuses on identifying and defining project problems through systematic analysis, laying the foundation for setting clear project objectives aligned with addressing these problems.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the importance of conducting thorough problem analysis in project planning.
- Learn techniques for identifying and defining project problems.
- Recognize the relationship between problem analysis and setting project objectives.

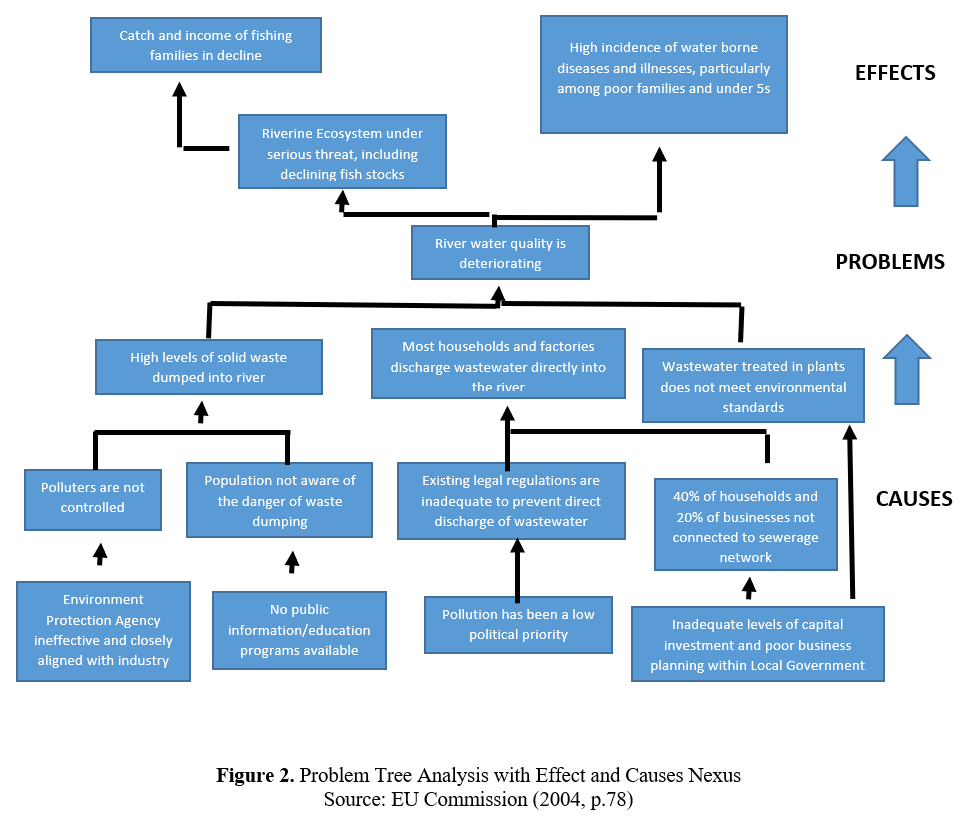
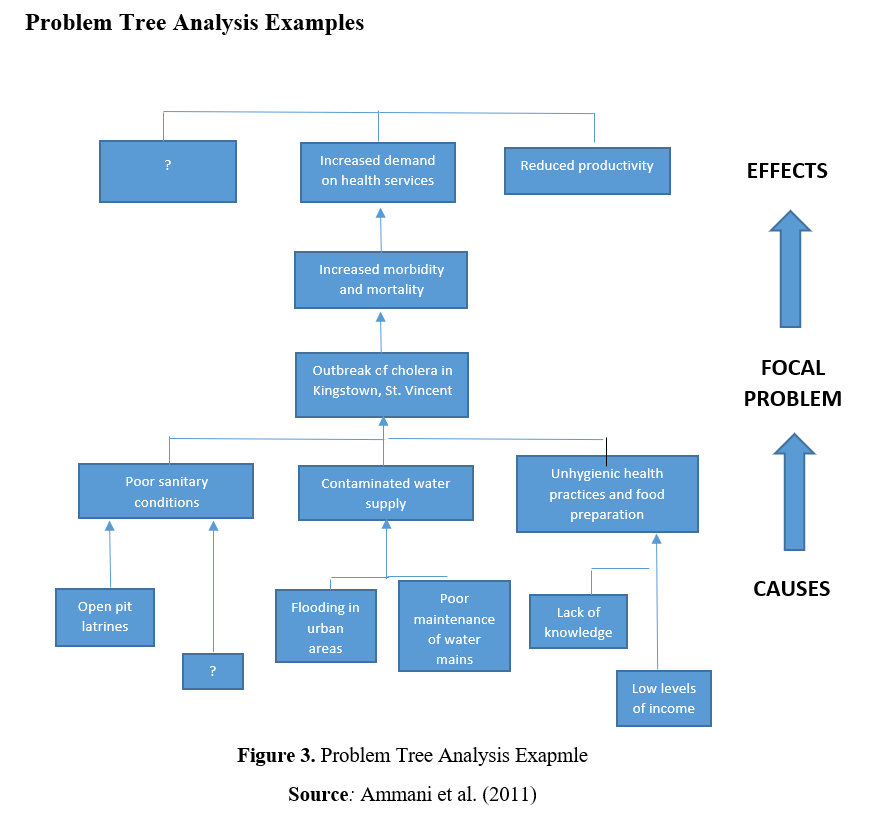
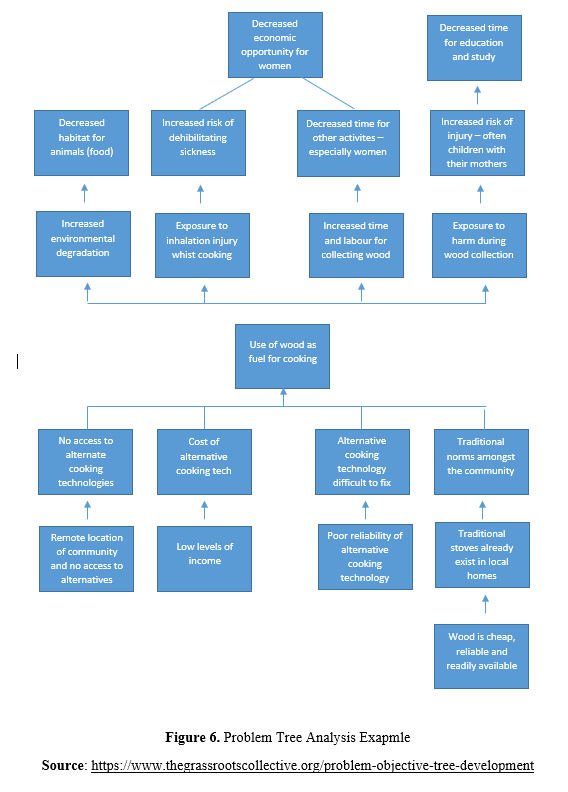
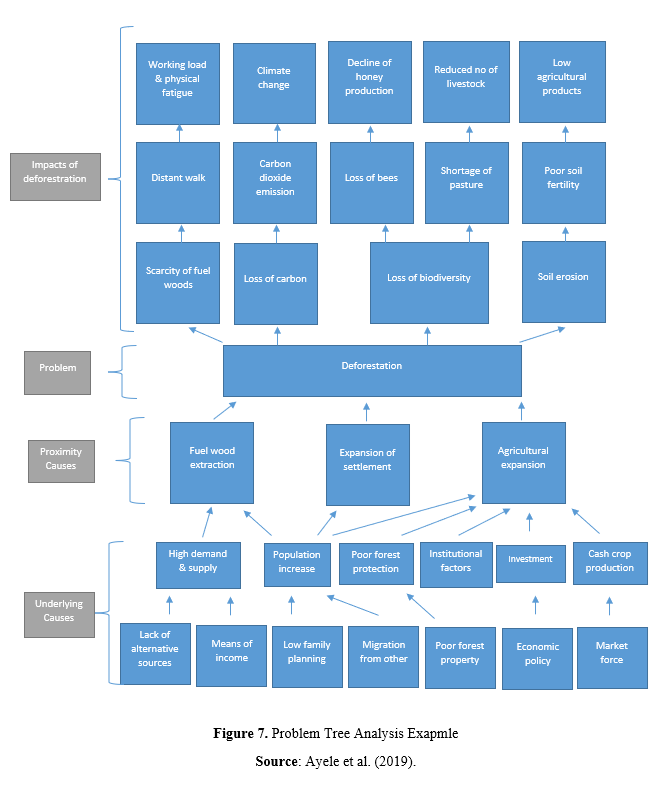
Problem tree analysis (also known as causes-and-effect diagram) is a useful method to see the root causes and effects of a problem together and to create goals and strategies accordingly (Mahto and Kumar, 2008, p. 22-23). It also allows for teamwork and creation of hierarchical order of problems and effects. In the middle of the problem tree is the main problem to which the project aims to intervene. Your main problem in the project, if solved, should contribute to the overall purpose of the project. In other words, the general purpose of the project will not directly include a problem that you will completely overcome during the project but will express a general situation targeting a negative situation resulting from the effects of this problem. For example, if you have identified youth unemployment as the main problem in your project, all of the goals and activities to combat this situation will contribute to the achievement of the overall goal. Therefore, your project will contribute to overall objective to a certain extent by addressing this problem.
You can also use a grant guide or call for proposals if you find it difficult to relate your main problem with the overall objective. Grant institutions and programs have their own priorities and objectives. You can use the sub-purposes of these programs while determining your general purpose. Thus, by referencing these goals, you also demonstrate the relevance of your project to the program. In this case, you can use these programme sub-objectives as they are, or you can use original sentences. On the other hand, you can define a unique overall objective using the tree you have created. In this case, you will need to briefly summarize the effects at the top of the hierarchy in a unique and comprehensive sentence. When we consider a grant program related to young people, an overall objective can be determined as follows: “to contribute to reduction of the social and economic disadvantage of young people and to improvement of their psychological well-being”.
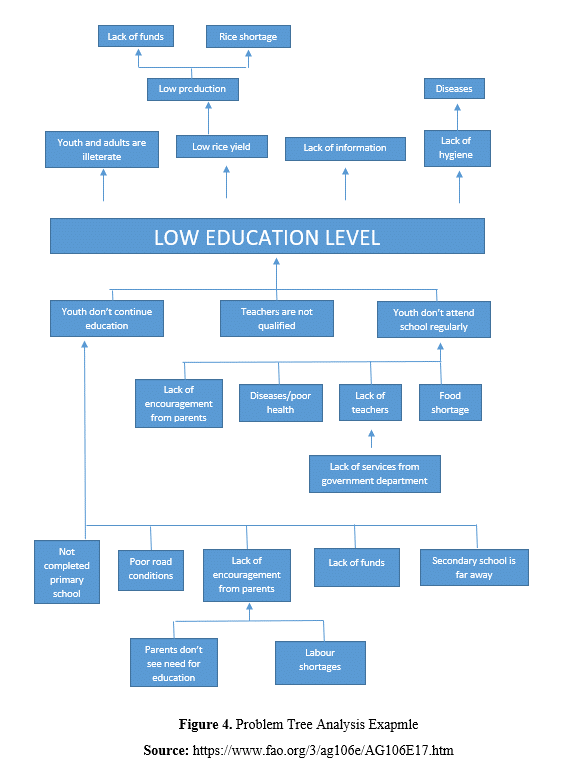
Once you have identified your main problem, you need to identify the factors that cause it. You should arrange which element causes which problem hierarchically by putting them in an order. If we take the example of youth unemployment in a region, lack of working experience may be one of the main reasons for youth unemployment. The reason for the lack of working experience can be listed as the lack of internship opportunities, the low number and capacity of companies in the field where young people graduate, the lack of basic communication skills among young people, the lack of career planning, support, and guidance for young people, etc.. Among these sub-problems, it is possible to make a more deep analysis. If we take the sub-problem of the lack of basic communication skills in young people as an example, the lack of adequate training in basic communication skills in schools, the lack of sufficient knowledge, skills and capacity of families about basic communication skills, the limited spaces and activities for socialization and communication can be listed as root problems. This sequencing can be performed and detailed until root causes are reached.
To the extent that the main problem is detailed, it will be able to be analyzed well, and targets and strategies can be determined. Planning the necessary activities for these goals and strategies is also related to a good analysis at this stage. The sub-problems you have identified will turn into activities that will be organized in order to reach the goals and objectives in the following stages (Vesely, 2008).
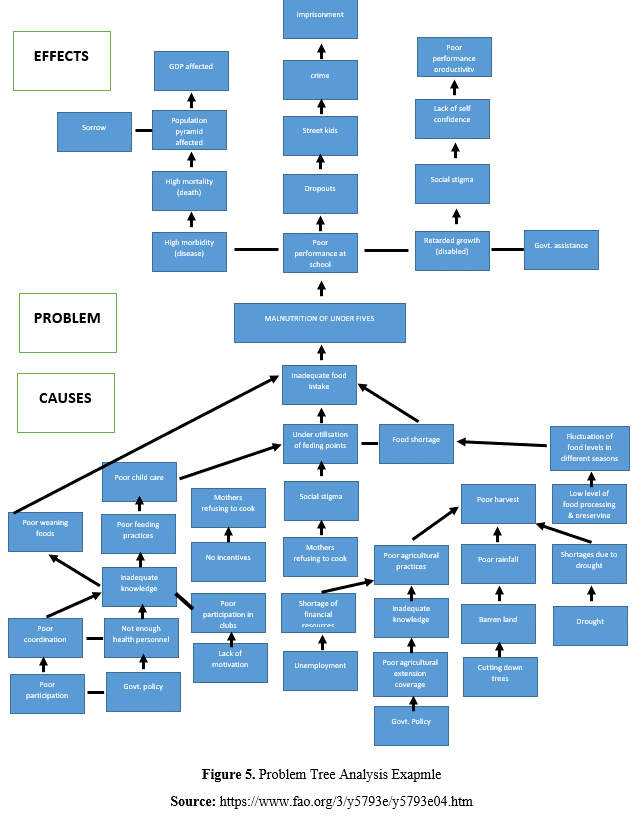
At the top of your main problem in the problem tree, there are the effects of this main problem. The effects you will detect should be detailed in the "impact" section of your project proposal form. For this reason, it is important to consider all effects and stakeholders while analyzing the problem at the first stage. Similar to the problem analysis, the more detailed the impact analysis, the more successful and comprehensive intervention logic will be put forward. This will enable you to detail the indicators you will determine in measuring the effects of your project and to measure the success in a more comprehensive and objective way. Again, if we were to give an example from the main problem of youth unemployment, this problem can lead to an increase in depression, in crime, in the use of harmful substances, cigarettes and alcohol, in social idle capacity, social exclusion of young people, and in jobs that require low qualifications rather than value-added jobs in the fields where young people are educated. These effects can be further deepened and detailed. For example, the emergence of depression in young people may cause an increase in suicide rates, a decrease in young people's expectations from life and hopelessness, an increase in depression drug use, an increase in psychologist / psychiatry services, etc..
The causes and effects of the main problem may also be related to more than one sub-cause and effect. In this case, connecting the items in your problem tree with arrows and lines will prevent confusion.