Information

Ensuring validity and reliability is crucial for the credibility of your study. For quantitative aspects, statistical tests for reliability can be employed, while for qualitative aspects, techniques like triangulation can be used (Lincoln & Guba, 1985).
Cronbach's alpha could be used to measure the reliability of the questionnaire, while the validity of qualitative data might be assessed through member checks.
In order to ensuring trustworthiness of qualitative research four main criteria as credibility, transferability, dependability and confirmability should be provided (Stahl and King, 2020). All researchers work on qualitative research, should prove that they implemented all phases of research design in accordance these criteria. These criteria can be summarized as Table 10.
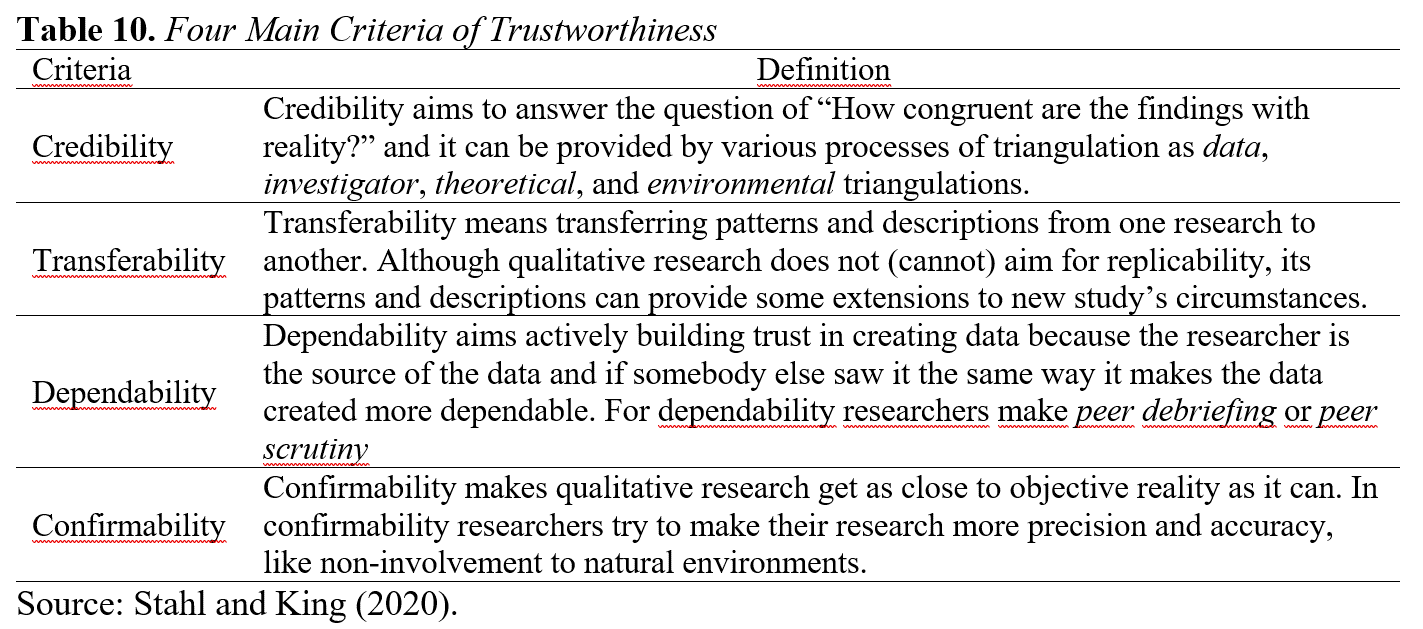
Table 10 summarizes the four basic criteria researchers apply for trustworthiness in qualitative research. These criteria: It is defined as credibility, transferability, dependability and confirmability. Credibility aims to determine how consistent the findings are with reality, and this can be achieved through various triangulation processes such as data, investigator, theoretical and environmental triangulation. Transferability refers to the ability to transfer patterns and descriptions from one study to another. Dependability aims to ensure that the researcher is a reliable source in the creation of data, and information is exchanged or evaluated with colleagues to increase reliability. Confirmability aims to match qualitative research to objective reality as much as possible, and researchers strive to further their research in terms of accuracy and precision.